GAPS IN THE INDIAN SOLAR TRAINING PROGRAMS
Solar energy has become one of the most sought after sources of power. The Government of India has set up an ambitious target of 100GW of solar power by the year 2022. The increase in solar power plant capacity is increasing at 100% year on year with the current capacity is close to 1.9 GW of solar power plant, both rooftop and utility scale combined. The solar inverter forms the important part of the entire solar photo voltaic power system. The inverter acts as the heart of the entire system. However, with the government is setting up ambitious targets for solar power plant capacity addition, the market is dominated by foreign brands and no Indian brand has a substantial market share. There are lot of training programs, supported by the Government and conducted independently in the area of solar energy. However, none of these programs cover the aspect of solar inverter manufacturing. The training programs cover the solar photo voltaic power system design and implementation, but not any aspect of manufacturing. With the Government of India promoting “Make in India” extensively, it is time that the right skills are imparted to the youth to manufacture world class solar inverters.
SOLAR ENERGY – AN INTRODUCTION
The sun is an important source for life to exist on this planet. Solar energy is the energy source derived directly from the sun. The energy from the sun is renewable, clean and does not cause any pollution. The solar energy is of two type viz., Solar Thermal and Solar Photo voltaic. Solar Photo voltaic is the process of converting sunlight into electrical energy with the help of solar photo voltaic panels. The solar photo voltaic panels convert the energy from the sun into electricity. Solar thermal is the process of converting sun’s heat in to either electrical energy or heat energy. Solar towers, parabolic dishes, concentrated solar collectors, evacuated tubes, flat plate collectors are some of the components that are used to convert sun’s heat into either electrical energy or heat energy.
SOLAR PHOTO VOLTAIC SYSTEM
Solar Photo voltaic system is used to convert the sunlight into electrical energy. A typical solar power plant comprises of Solar panels, Solar Inverters, Junction boxes, mounting structures, cables, grounding components and lightning arrestors. The solar panels convert the light energy into DC electricity.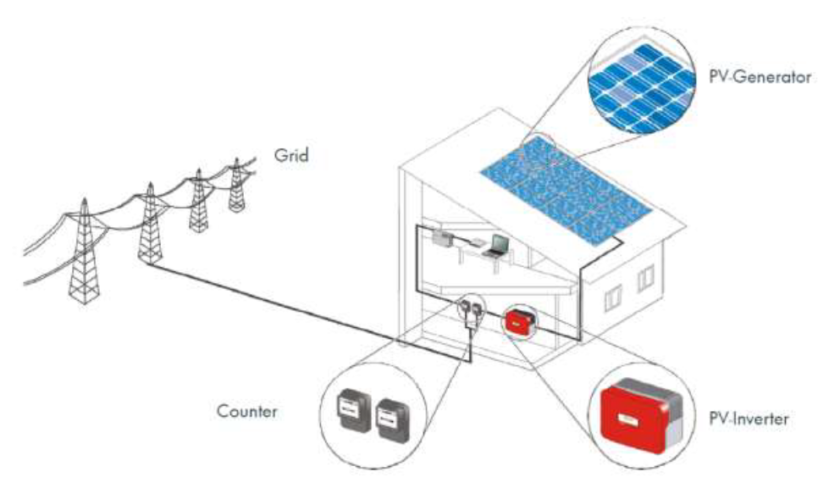
A Typical Solar Power Plant set up
(Source: SMA Solar Academy power point presentation)
The solar inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity which is used by us in our day-to-day applications. The solar inverter is considered to be the brain of the entire system as it is the interface between the solar panels and the load connected. The solar inverters play a crucial role in the optimized performance of the entire system. The inverter ensures the system efficiency is high, easy functioning of the system, maximum reliability.
MARKET SEGMENT
The solar photovoltaic market is categorized into two segments viz., rooftop and utility scale.
Rooftop Market
Rooftop installations are those in which solar panels are mounted on the top of the roof of a building. The power produced from these panels are usually used by the roof owner for captive consumption, selling the remaining power to the electricity board
Utility scale Market
Utility scale is where the installations are made on the ground level and the power is sold to the electricity board, distribution licensee or to private companies through the electricity board.
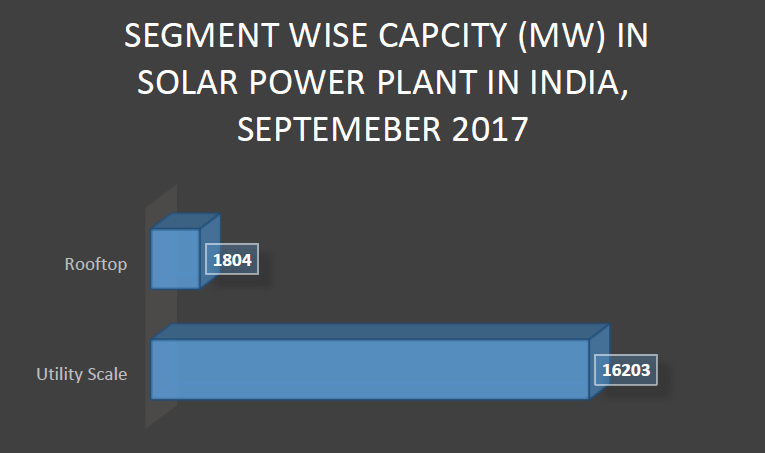
Source: Bridge to India Solar Map and Solar Rooftop Map reports September 2017
SOLAR INVERTER MARKET SHARE
The solar inverter which plays a crucial role in a solar photo voltaic power system is majorly supplied by foreign brands. Indian brands lie far behind from their global counterparts. The Indian solar manufacturers have a say at least in the roof top solar market. However, when it comes to the utility scale solar market, the foreign brands completely dominate the market share.
Rooftop Market share
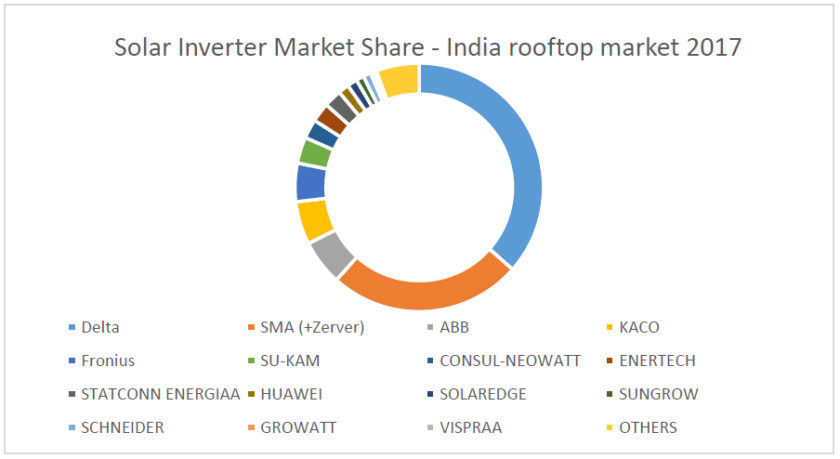
Make | Market Share | Country of Origin | Direct Indian presence |
Delta | 36.40% | Taiwan | Gurgaon |
SMA (+Zever) | 25.10% | Germany | Mumbai |
ABB | 5.90% | Switzerland | Bangalore – direct |
KACO | 5.60% | Germany | India |
Fronius | 5% | Austria | Pune |
SU-KAM | 3.40% | India | |
CONSUL-NEOWATT | 2.50% | India | Regional office |
ENERTECH | 2.50% | India | Regional office |
STATCONN ENERGIAA | 2.30% | India | Noida |
HUAWEI | 1.40% | China | Chennai |
SOLAREDGE | 1.30% | Israel | Bangalore – direct |
SUNGROW | 1.00% | China | Gurgaon |
SCHNEIDER | 1.00% | Canada | Bangalore – direct |
GROWATT | 0.40% | China | Chennai |
VISPRAA | 0.40% | India | |
OTHERS | 5.60% |
Source: Bridge to India reports on India solar map 2017 and respective company websites
As it is clear from the table Indian players have only 11.10% percentage of the market share in the rooftop solar market.
Utility scale Market Share
The Indian players have no place in the market share in the utility level segment. The utility market where there is no share for Indian solar inverter manufacturers is way higher than the rooftop market where the Indian solar inverter manufacturers have 11.10% of the market share. As listed above, the rooftop is installed capacity is a mere 1804 MW as against 16,203 MW in the utility scale segment.
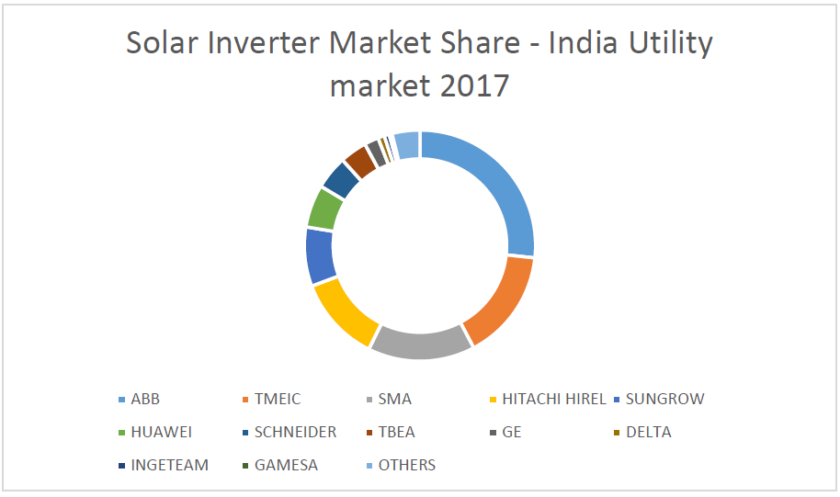
Make | Market Share | Country of Origin | Direct Indian Presence |
ABB | 26.70% | Switzerland | Bangalore – direct |
TMEIC | 15.60% | Tokyo, Japan | Bangalore – direct |
SMA | 15% | Germany | Mumbai |
HITACHI HIREL | 12% | Japan / India | regional offices |
SUNGROW | 8.30% | China | Gurgaon |
HUAWEI | 6% | China | Chennai |
SCHNEIDER | 4.70% | Canada | Bangalore – direct |
TBEA | 3.80% | China | |
GE | 2% | global | india |
DELTA | 0.90% | Taiwan | Gurgaon |
INGETEAM | 0.70% | China | Gurgaon |
GAMESA | 0.40% | Spain | |
OTHERS | 3.90% |
Source: Bridge to India reports on India solar rooftop map 2017 and respective company websites
THE CURRENT TRAINING PATTERN
The current training pattern s more focused on the system design and installation and not on the solar inverter manufacturing. A typical solar training program syllabus looks as below.
- Basics of electricity
- Basics of energy
- Renewable energy – overview
- Solar Energy – Introduction
- Types of solar energy
- Genesis of Photo voltaic technology
- Solar Photo voltaic – Introduction
- Solar thermal – introduction
- Solar photo voltaic – components
- Solar panel – manufacturing
- Solar PV – System design (off grid and On Grid)
- Solar PV – Installation
- Solar PV – Business and Employment opportunities
- Solar PV – Government schemes
- Solar PV – Financing opportunities
- Solar PV – Detailed Project Report Preparation
- Solar PV – Sales & Marketing
As it is evident from the above content, there is no training programs on manufacturing of solar inverter. It is high time, the government takes appropriate steps to train the youth to manufacture world class solar inverters.
CONCLUSION
The Indian manufacturers need to raise their standards to international level so that the Indian solar inverters are accepted locally first followed by global acceptance. In order to achieve this proper skills to manufacture world class solar inverters are to be imparted to the youth who in turn can become entrepreneurs manufacturing solar inverters and can become highly skilled employees in Inverter manufacturing companies.